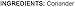Food to Live Cumin Seeds Whole (1 Pound)
Appliances
Arts, Crafts & Sewing
Automotive
Baby
Beauty
Books
CDs & Vinyl
Collectibles & Fine Arts
Cell Phones & Accessories
Clothing, Shoes & Jewellery
Computers
Electronics
Health & Personal Care
Home & Kitchen
Industrial & Scientific
Luggage & Travel Gear
Musical Instruments
Office Products
Patio, Lawn & Garden
Pet Supplies
Software
Sports & Outdoors
Tools & Home Improvement
Toys
Video Games